These directions are applicable for at least Linux Mint 19, 20, and 21 using our USB-A 3.0 Data Transfer Cable for GNU/Linux (TPE-3TRANCBL). If you need directions for other versions of Linux Mint contact support. Also, consider checking out the video demonstration of this tutorial.
Before you begin make sure you don't have a firewall enabled or the below directions won't work.
Computer 1: On the new system open the Software Manager, install openssh-server, and setup the data transfer cable network connection
1. From the Linux Mint menu go to Administration > Software Manager, search for openssh-server, click on openssh-server, click the Install button, and enter your password to authenticate
2. Plug in one end of the Data Transfer Cable to a USB 3.0 port (preferably, usually blue) or USB 2.0 port if a 3.0 port is unavailable
3. Go to the network applet in the lower right corner and select Network Connections
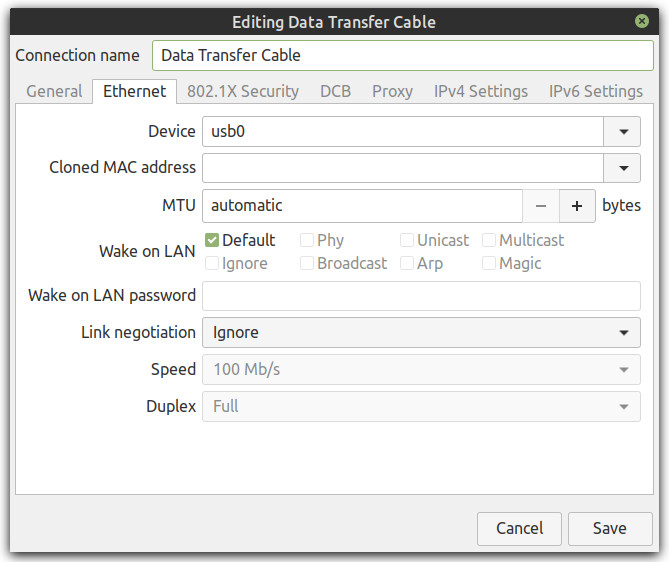
4. Click the + button to add a new network connection
5. Select Ethernet from the drop down and the Create... button
6. For the Connection name enter Data Transfer Cable
7. Under the Ethernet tab select usb0 from the Device drop down box or whatever the Data Transfer Cable shows up as
8. Next click on the IPv4 Settings tab
9. Click on the Method drop down box and select Shared to other computers
10. Click the Save button
11. From the network applet in the lower right corner select the Data Transfer Cable connection
12. While in the network applet disconnect from any other wireless or wired network connections
Computer 2: On the old/other system open the Software Manager, install Filezilla, and connect
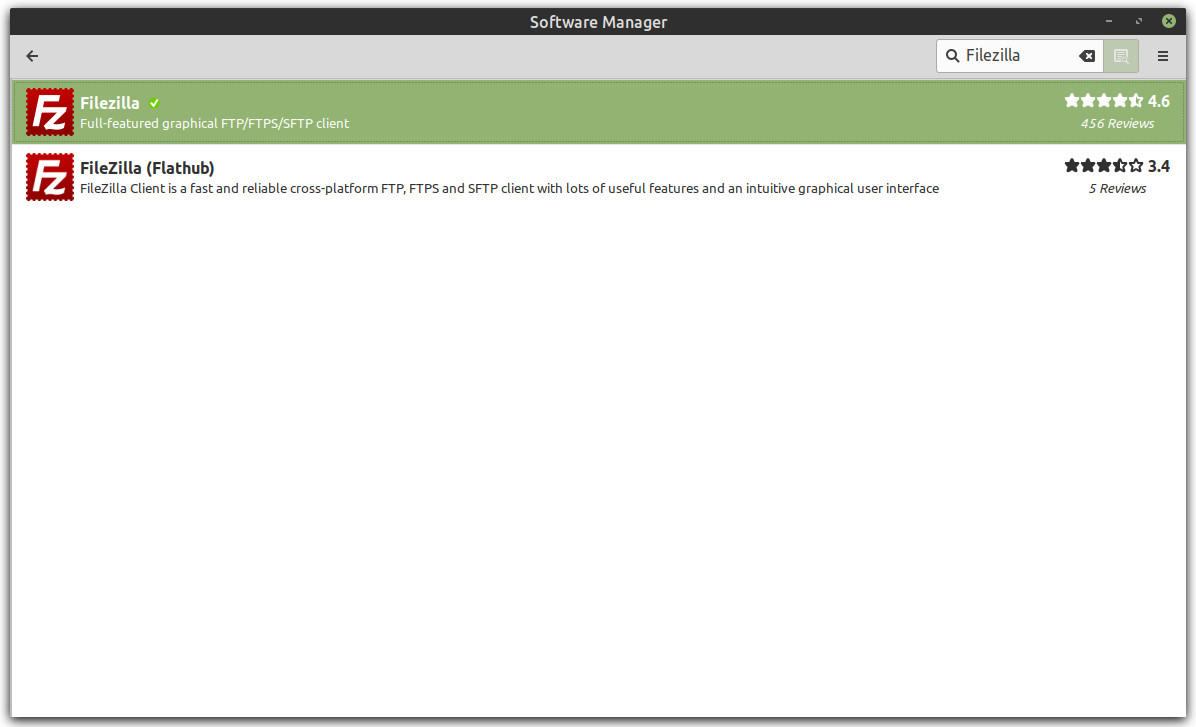
1. From the Linux Mint menu go to Administration > Software Manager, search for Filezilla, click on Filezilla, click the Install button, enter your password to authenticate and install, and finally click the Launch button to start Filezilla
2. Go to the network applet in the lower right corner and disconnect from any wireless connections
3. Plug in the other end of the Data Transfer Cable to a USB 3.0 port (preferably, usually blue) or USB 2.0 port if a 3.0 port is unavailable
4. When connecting the Data Transfer Cable the default behavior in Linux Mint is to connect to the new network, but if nothing happens you can also create a new network connection by following steps 2-11 minus steps 7-9 as was done with in the instructions for computer 1
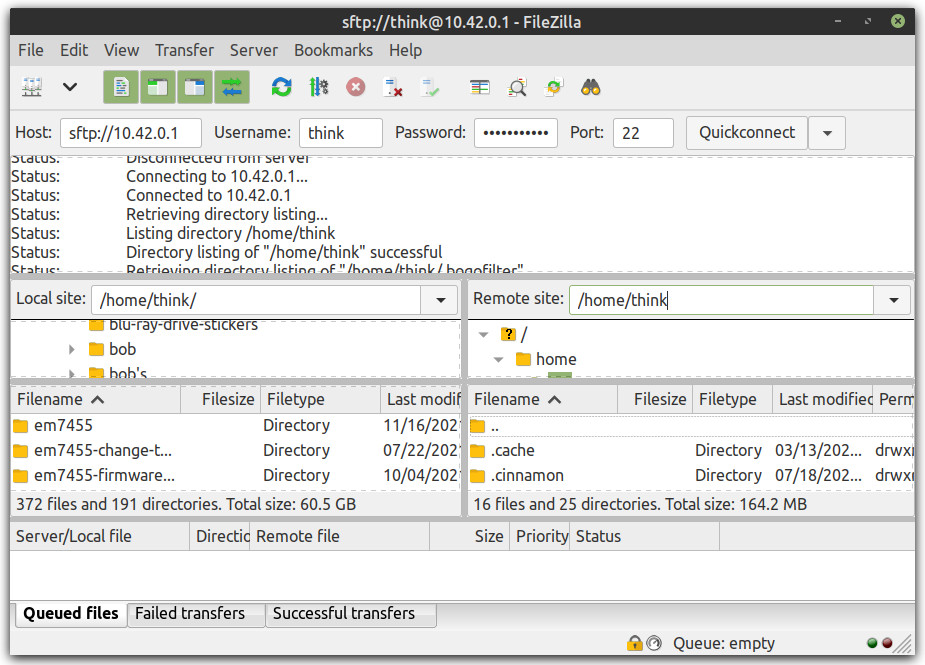
5. Back in Filezilla you will need to enter the Host name or IP address of Computer 1, which should be 10.0.42.1 although you can verify this by going to the Network Applet in the lower right of Computer 1 > Network Settings > USB Ethernet (or if multiple USB Prolific Ethernet) and copying the IPv4 Address to Filezilla's Host name box
6. In Filezilla's Username box you will need to enter the login username you use on Computer 1
7. In Filezilla's Password box you will need to enter the password the login username you use on Computer 1
8. In Filezilla's port box you can enter the default sftp port of 22
9. Now click the Quickconnect button in Filezilla
10. You can now drag and drop files and folders from the local computer (Computer 2) to the remote computer (Computer 1)
There is one last thing that is generally a good idea to do. After transferring your files to a new computer remove openssh-server. This is mostly a security precaution as anyone can get into your machine remotely if your not utilizing a strong enough password. To remove openssh-server click on the Linux Mint menu icon in the lower left of the screen and go to Administration > Software Manager, search for openssh-server, and click on the remove button, and enter your password to authenticate.
